Linear Sensor are critical to the performance to their sensitivity and linearity over their specified operating temperature range and immune to most environmental disturbance that may affect optical or mechanical devices, such as vibration, moisture, dirt or oil films, ambient, lightning, etc.
Linear Hall Effect Sensor are commonly used in current sensing, power sensing (watt-hour-metering), current trip-point detection, strain gauge, biased (magnetically) sensing applications, Ferrous metal detection, proximity sensing, Joy-Stick with intermediate positions sensing, liquid-level sensing, temperature / pressure / vacuum sensing, throttle or air valve positions sensing, non-contact potentiometers, etc.
Components Required
- Raspberry Pi / Banana Pi / Orange Pi (If your using Banana Pi or Orange See first the GPIO Pins)
- Hall Effect Sensor
- LED (Any Color)
- 220 Ohms Resistor
- Solder Less Bread Board
- Jumper Wire / DuPont Wire
- 10k Resistor (Optional)
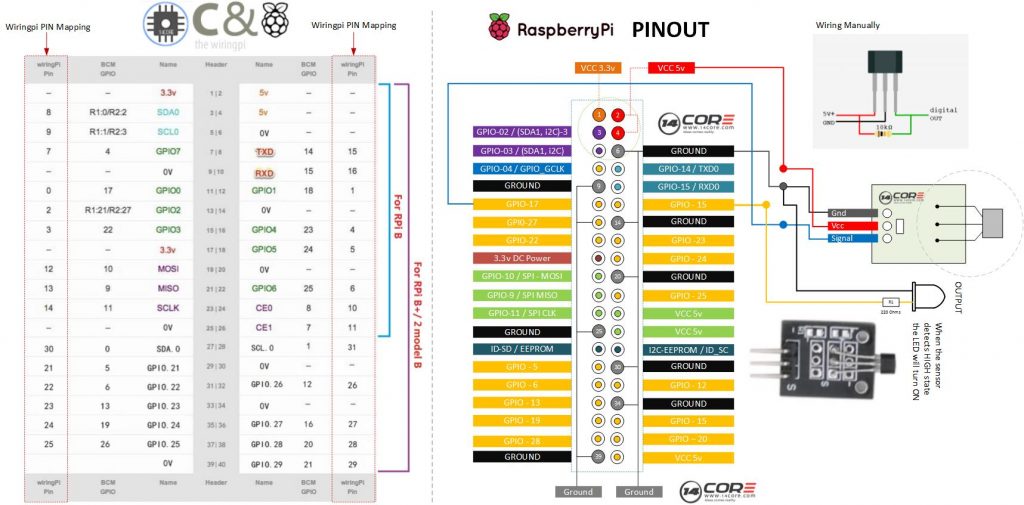
Wiring Diagram
For C Code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 |
/* 14CORE Test Code for: Hall Effect Switch on C Code .:+osysso++:` `+yhs/-` `-+s+` `:/+++++++++` .:/++ooo++/-` .ooooooooooo+: :///////////- `odh/` `:y+` /ddhsooooooo+ /hddhsooooydddh sdddoooooosdddy` `////////////` -hds` `sy. +ddy` .ddd: sddy.dddo +ddd- .-----------` `hds :sssss/ -ossssso-yy` `hdd: oddy `ddd/oddd:......+dddo .++++++++++++ +dd` :sdddh` :ydddddddo +y/ .ddd+........ `hddy:.....:yddy.hdddddddddddy+. ```````````` ydy .hddd/+hdddhydddh/.+yo /hdddddddddd. :shddddddddhs/`+ddd:````-yddy- :ooooooooooo+ odh` sdddooyyyyyhddddyy.sy+ ` `......... ``.... ....` ```...` ` `` `` ` -dd+`::::` .:::- /yy. -oos+:-oos+--oos+: /o `+y o/: o:+/ h:`yos /+-`/+/+ s:y/y. /dd/ `+yy: +//+ +/:+ +/:+ -. `/ -:o.:/:`//+- + +:- :`-+:`://: +`o`+. -yds. `/yys- .`-.. .``` ```` .`` ` ` ``` ``-..` ` :ydy/.`````.-/oyhs: `+++oo+oo+:.+-++/-/ooo+o +:o/oo///:+/ .:oyhhhhhhhso:` `. ``` */ #include <wiringPi.h> #include <stdio.h> #define SensorPin 0 #define LedOutput 1 void INOUT(char* ledstate) { pinMode(Rpin, OUTPUT); if (ledstate == "OUTPUT") { digitalWrite(LedOutput, HIGH); } else if (ledstate == "INPUT") { digitalWrite(LedOutput, LOW); } else printf("Error Led Output"); } int main(void) { if(wiringPiSetup() == -1) //If no response from wiringpi.h print { printf("Wiring Pi Initialization Faild"); return 1; } pinMode(SensorPin, INPUT); INOUT("INPUT"); while(1){ if(0 == digitalRead(SensorPin)){ delay(10); if(0 == digitalRead(SensorPin)){ INOUT("OUTPUT"); printf("Detected!\n"); } } else if(1 == digitalRead(SensorPin)){ delay(10); if(1 == digitalRead(SensorPin)){ while(!digitalRead(SensorPin)); INOUT("INPUT"); } } } return 0; } |
For Python Code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 |
# 14CORE Test Code for: Ball Tilt Switch on Raspberry Pi # .:+osysso++:` # `+yhs/-` `-+s+` `:/+++++++++` .:/++ooo++/-` .ooooooooooo+: :///////////- # `odh/` `:y+` /ddhsooooooo+ /hddhsooooydddh sdddoooooosdddy` `////////////` # -hds` `sy. +ddy` .ddd: sddy.dddo +ddd- .-----------` # `hds :sssss/ -ossssso-yy` `hdd: oddy `ddd/oddd:......+dddo .++++++++++++ # +dd` :sdddh` :ydddddddo +y/ .ddd+........ `hddy:.....:yddy.hdddddddddddy+. ```````````` # ydy .hddd/+hdddhydddh/.+yo /hdddddddddd. :shddddddddhs/`+ddd:````-yddy- :ooooooooooo+ # odh` sdddooyyyyyhddddyy.sy+ ` `......... ``.... ....` ```...` ` `` `` ` # -dd+`::::` .:::- /yy. -oos+:-oos+--oos+: /o `+y o/: o:+/ h:`yos /+-`/+/+ s:y/y. # /dd/ `+yy: +//+ +/:+ +/:+ -. `/ -:o.:/:`//+- + +:- :`-+:`://: +`o`+. # -yds. `/yys- .`-.. .``` ```` .`` ` ` ``` ``-..` ` # :ydy/.`````.-/oyhs: `+++oo+oo+:.+-++/-/ooo+o +:o/oo///:+/ # .:oyhhhhhhhso:` `. ``` #!/usr/bin/env python import RPi.GPIO as GPIO TiltSensorPin = 11 #Sensor is connected to GPIO 17 LedOutputPin = 12 #Output led connected to GPIO 15 Led_status = 1 def setup(): GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # GPIO will be numbered GPIO.setup(LedOutputPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set LedOutputPin's mode is output GPIO.setup(TiltSensorPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) GPIO.output(LedOutputPin, GPIO.HIGH) # Set LedOutputPin high def swLed(ev=None): global Led_status Led_status = not Led_status GPIO.output(LedOutputPin, Led_status) # switch led status(on-->off; off-->on) if Led_status == 1: print '14CORE | OUTPUT LED TURN OFF' else: print '14CORE | OUTPUT LED TURN ON' def loop(): GPIO.add_event_detect(TiltSensorPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=swLed) # wait for falling while True: pass # Do nothing def destroy(): GPIO.output(LedOutputPin, GPIO.HIGH) # Led will turn On GPIO.cleanup() # Rlease or clean resource if __name__ == '__main__': setup() try: loop() except KeyboardInterrupt: # When press control C child program will distroy destroy() |






Pingback:Wiring the 14CORE 37 Sensors for Arduino & Raspberry Pi | 14Core.com
You show the output of the 3144 Hall sensor pulled up to +5 Volts and then connected to GPIO17.
Be aware that the GPIO pins of a Raspberry Pi are not 5 volt tolerant. You should never connect them to +5 Volts! Many people have done this. Many people have damaged their Pi.
Remove the 10k resistor and use the internal GPIO pullup to power the open collector output of the Hall sensor.
But never, ever, connect a GPIO pin to +5 Volts.